Função/notação matemática para descrever a ordem de grandeza/crescimento de um algoritmo conforme n (sendo n o parâmetro/tamanho da entrada).
O = Omicron
Análise assintótica / Matemática assintótica Uma analise uniforme/abstrata.
n^2
- Somar cada passo
- Ignore as contantes
- Ignore os fatores multiplicativos
- Ignore os fatores de menor crescimento
Como a função escala no tempo de acordo com seus parametros de entrada.
Big-O sempre espera o pior cenário.
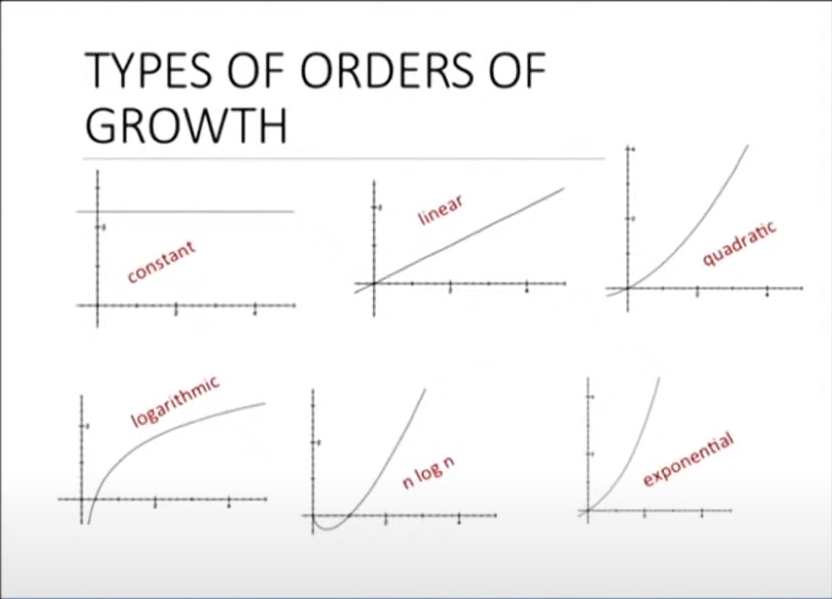
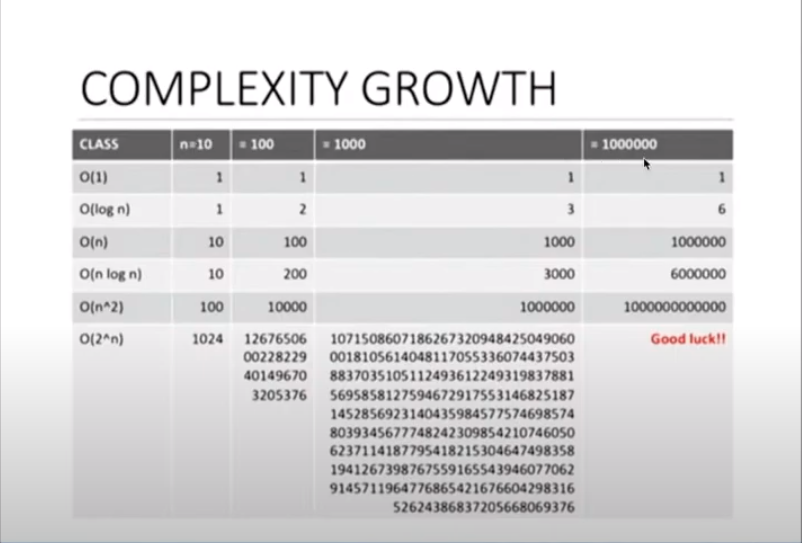
- Constante
O(1) - Logarítmica
O(log n) - Linear
O(n) - Log-Linear
O(n log n) - Quadrática
O(n^2) - Exponencial
O(2^n)
Eixo X = tamanho entrada - Eixo Y = tempo
Sempre vai levar o mesmo tempo independente do tamanho da entrada.
Exemplo de algoritmo:
"""
Celsius/Fahrenheit Calculator
"""
def c_to_f(c):
return c*9.0/5 + 32
c_to_f(40)
# 104
Logpor padrão se não é passado a base assume o valor 2.
Log 8 = xmesma coisa que2 ^ x = 8
Exemplo de algoritmo:
"""
Bisect search - funciona em listas ordenadas, dividindo o problema sempre em partes menores.
"""
def bisect_search(L, e):
def helper(L, e, low, high):
if high == low:
return L[low] == e
mid = (low + high) // 2
if L[mid] == e;
return True
elif L[mid] > e:
if low == mid: #nothing left to search
return False
else:
return helper(L, e, low, high - 1)
else:
return helper(L, e, mid + 1, high)
if len(L) == 0:
return False
else:
return helper(L, e, 0, len(L) -1)
L = [1,3,3,4,4,5,5,7,8,8,9,9,11,13,20]
bisect_search(L, 7)
# TrueVai aumentando linearmente em função de n.
Exemplos de algoritmo:
"""
Fatorial
"""
def factorial(n):
answer = 1
while n > 1:
answer *= n
n -= 1
return answer
factorial(5)
# 120"""
Busca linear em uma lista não ordenada
"""
def linear_search(L, e):
found = false
for i in range(len(L)):
if e == L[i]:
found = True
return found
L = [1,4,8,3,7,4,9,13,5,9,3]
linear_search(L, 10)
# FalseExemplo de algoritmo:
"""
Implementa o merge sort
"""
def merge_sort(L):
def merge(left, right):
result = []
i,j = 0,0
while i < len(left) and j < len(right):
if left[i] < right[j]:
result.append(left[i])
i += 1
else:
result.append(right[j])
j += 1
while (i < len(left)):
result.append(left[i])
i += 1
while (j < len(right)):
result.append(right[j])
j += 1
return result
if len(L) < 2:
return L[:]
else:
middle = len(L)//2
left = merge_sort(L[:middle])
right = merge_sort(L[middle:])
return merge(left, right)
L = [1,4,8,3,7,8,4,9,13,5,11,20,5,9,3,5,9,8,3,8,8,2,7,10,13,19,9]
merge_sort(L)
# Exemplo de algoritmo:
"""
Determina se uma lista é subset de outra.
"""
def is_subset(L1, L2):
for e1 in L1:
matched = False
for e2 in L2:
if e1 == e2:
matched = True
break
if not matched:
return False
return True
L2 = [1,4,8,3,7,4,9,13,5,11,20]
L1 = [5,9,3]
is_subset(L1, L2)
# TrueExemplo de algoritmo:
"""
Gera o powerset de um determinado conjunto.
"""
def powerset(L1, L2):
res = []
if len(L) == 0:
return [[]]
smaller = powerset(L[:-1])
extra = L[-1:]
new = []
for small in smaller:
new.append(small + extra)
return smaller + new
L = [1,3,5,7]
powerset(L)
# [
# [],
# [1],
# [3],
# [1,3],
# [5],
# [1,5],
# [3,5],
# [1,3,5],
# [7],
# [1,7],
# [3,7],
# [1,3,7],
# [5,7],
# [1,5,7],
# [3,5,7],
# [1,3,5,7]
# ]